
Blog Detail
Good Distribution Practice for Medical Devices (CDAKB) Requirements in Indonesia

Good Distribution Practice for Medical Devices (CDAKB) Requirements in Indonesia In Regulation of the Minister of Health Number 62 of 2017, medical devices are defined as " ...instruments, apparatus, machines and/or implants that do not contain drugs used to prevent, diagnose, cure and alleviate disease, treat sick people, restore health in humans, and/or form structures and improve body functions."
The classification of Medical Devices is as follows:
Electromedical Health Devices are medical devices that use an AC or DC power source to operate.
Radiation Electromedical Health Devices are medical devices that use an AC or DC power source to operate and emit ionizing radiation or radioactive substances during use to achieve their intended use.
Non-Radiation Electromedical Health Devices are medical devices that use an AC or DC power source for operation and do not emit ionizing radiation or radioactive substances during use to achieve their intended use.
Non-Electromedical Sterile Medical Devices are medical devices that do not require an AC or DC power source with a sterilization process in their production process, thus producing sterile products such as syringes, sterile gauze, surgical thread, IV catheters, and infusion sets.
Non-sterile medical devices are medical devices that are not sterile and do not require AC or DC power, such as plasters, surgical instruments, baby scales, manual wheelchairs, manual patient beds, and stethoscopes.
In Vitro Diagnostic Products are medical devices used for In Vitro examination of specimens from inside the human body to provide information for the diagnosis, monitoring, or a combination. It includes reagents, calibrators, control materials, specimen containers, software, and other related instruments, tools, or chemicals, such as blood sugar test kits, young pregnancy tests, uric acid tests, clinical chemistry test kits, and a hematology analyzer.
Based on the Regulation of the Minister of Health Number 4 of 2014, "Good Distribution Practice for Medical Devices, later abbreviated as CDAKB, are guidelines used in a series of distribution and quality control activities aimed at ensuring that distributed medical device products meet the requirements set according to their intended use."
Good Distribution Practice for Medical Devices "CDAKB" was commenced in 2014 as a practical requirement for medical device distributor companies by the Ministry of Health in Indonesia. After six years, in 2020, CDAKB finally became a mandatory requirement for all medical device distribution in Indonesia. The target set by the government regarding the proportion of medical equipment distribution facilities that have been CDAKB certified in 2022 is 30%, 60% (2023), and 90% (2024). CDAKB is only valid for five years, thereby, it needs to be periodically renewed.
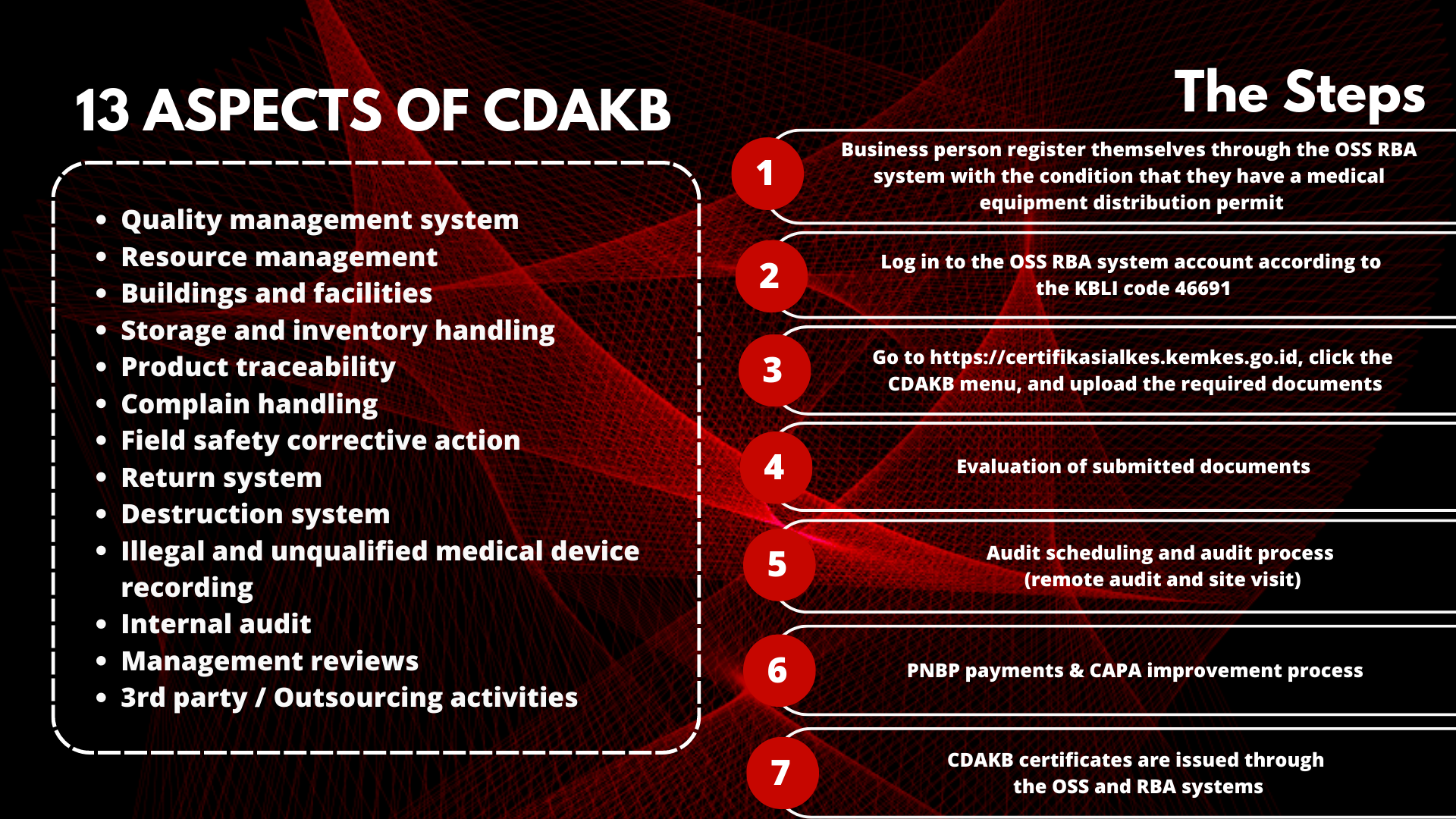
13 Aspects of Good Distribution Practice for Medical Devices (CDAKB)
Quality management system
Resource management
Buildings and facilities
Storage and inventory handling
Product traceability
Complaint handling
Field safety corrective action
Return system
Destruction system
Illegal and unqualified medical device recording
Internal audit
Management reviews
3rd party / Outsourcing activities
CDAKB is a mandatory component for companies that have distribution permits or IDAK. Thus, companies should renew the permit by attaching a completion of CDAKB certification. The following documents need to be prepared for CDAKB certification:
Distribution Permit (IDAK)
NIB
Organizational structure, job descriptions, roles, responsibilities, and authorities of related positions.
PJT-related documents
Warehouse and office layout and photo documentation with timestamp
The format of the type of lakes distributed
SK Internal Audit Team, MR, ReCall Assignment
Fixed procedures related to 13 aspects
Acceleration Strategy There are four classifications of distributor types regarding the acceleration of CDAKB certification. Those are (1) distribution license holders; (2) distribution permit owners (1-3 medical device groups); (3) distribution permit holders (4-5 medical device groups); (4) and ISO certifications 9001 and 13485. This acceleration is for sub-distribution permit owners and companies certified with ISO 9001-2015 and ISO 13485-2016 accredited by KAN that are no longer subject to on-site audits.
In addition, one of the efforts to accelerate the Ministry of Health is the self-assessment instrument. This instrument is a checklist form for companies to check their fulfillment of the requirements before verification by the evaluator.
CDAKB certification application flow
Business actors register themselves through the OSS RBA system with the condition that they have a medical equipment distribution permit
Log in to the OSS RBA system account according to the KBLI code 46691
Go to https://certifikasialkes.kemkes.go.id, click the CDAKB menu, and upload the required documents
Evaluation of submitted documents
Audit scheduling and audit process (remote audit and site visit)
PNBP payments
CAPA improvement process
CDAKB certificates are issued through the OSS and RBA systems
PT Inspiry Indonesia Konsultan provides CDOB certification assistance services from the beginning until the certificate is released. PT Inspiry Indonesia Konsultan offers a complete assistance program, starting from document preparation to permit issuance.
Contact us via:
E-mail: inspiryindonesiakonsultan@gmail.com
Website: www.inspiryconsultant.com
Instagram: @inspiry.indonesia
Mobile: +62 877 6777 1778
Salam Inspirasi,
apt. Syifa Amirta Sani, S. Farm
